Requirement
NIST SP 800-171 REV.2 / CMMC 2.0 Level 2 - Control - CM.L2-3.4.5 – Define, document, approve, and enforce physical and logical access restrictions associated with changes to organizational systems.
Understanding the Requirement
This control in NIST SP 800-171 REV.2 / CMMC 2.0 Level 2 requires you to specify who may make changes to your systems, record those permissions, gain explicit approval for both the people and the times when changes occur, and enforce both physical and logical restrictions so only authorized personnel can perform approved changes. In practice that means creating and maintaining a list of authorized change agents, documenting their physical access (for example, server room or cabinet access) and logical access (accounts, roles, and systems), approving change windows and personnel through a formal process, and enforcing those decisions with technical and physical controls plus logging and periodic review.
Technical Implementation
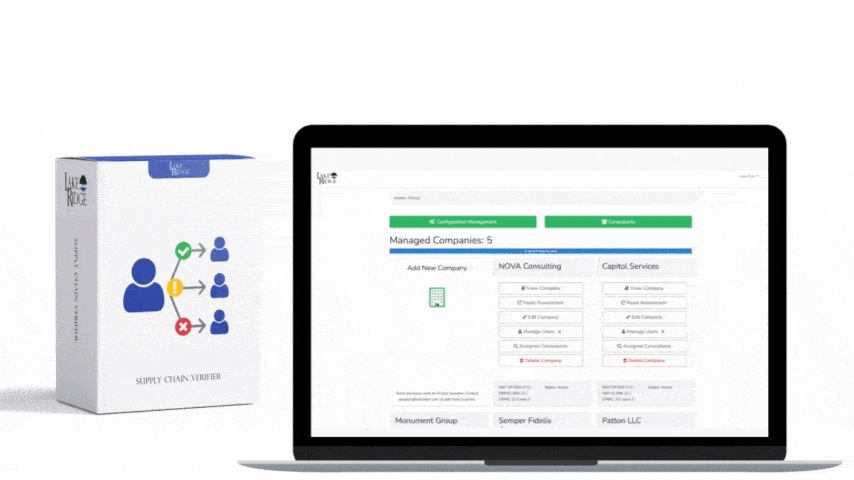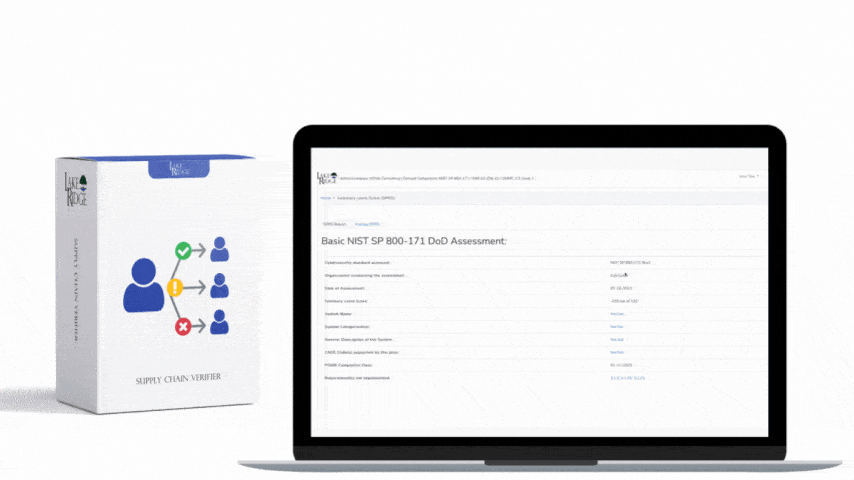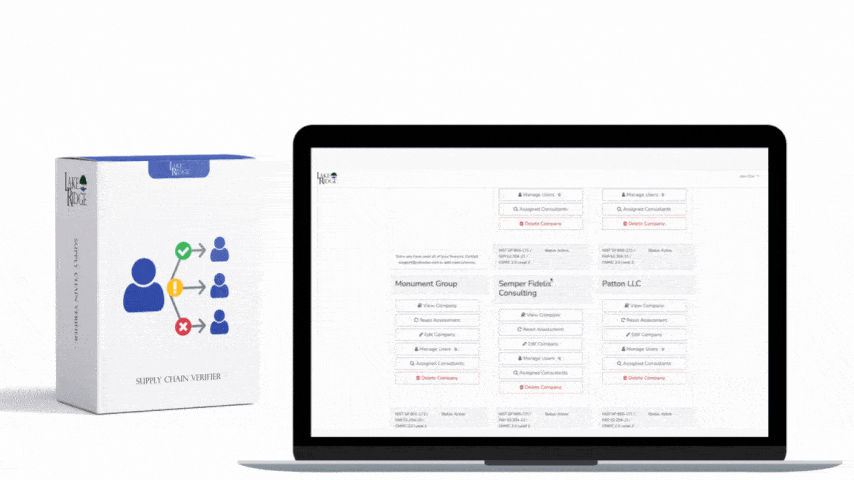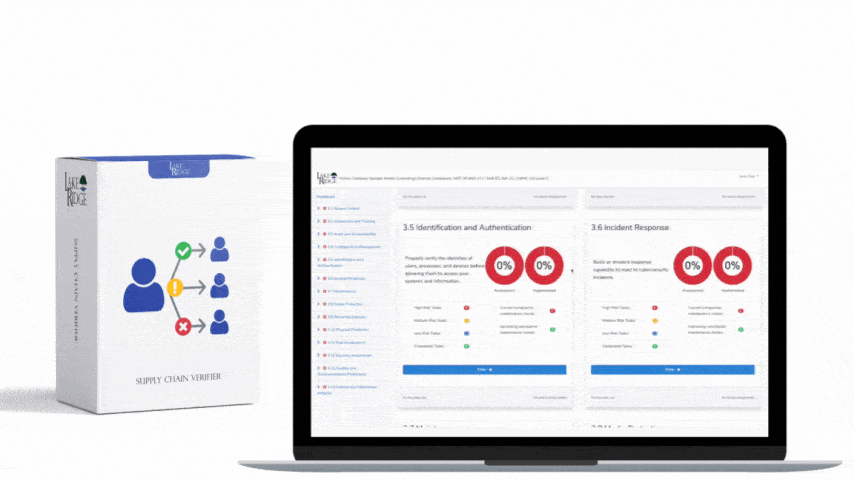
- Inventory authorized change agents: Maintain a living document (access authorizations) listing individuals and job roles permitted to make changes. Record the scope of their permissions (which systems, which environments—prod vs. test) and include contact details and approvals. Store the document in a controlled location and include version history.
- Define and document physical restrictions: Specify physical controls required for change activities (badge access to the server room, locked racks, escort requirements, CCTV coverage). Include which people have badge privileges, key custody rules, and where physical keys are logged. Tie physical access records to your change authorization document.
- Define and document logical restrictions: Create an access matrix that maps roles to systems, accounts, and permitted actions (deploy, rollback, configuration change). Apply least-privilege and separation of duties: use role-based access control (RBAC), dedicated deployment accounts, and temporary elevation mechanisms for privileged tasks.
- Enforce through technical controls: Use MFA, privileged access management (PAM) or just-in-time elevation, jump hosts for administrative access, and network segmentation so change actions require authenticated, auditable paths. Implement time-based controls if your policy limits changes to defined windows (e.g., change controls that only allow deployments during approved hours).
- Approval and change workflow: Require a formal change request (ticket) with documented approvers before execution. Implement a lightweight Change Advisory Board (CAB) for higher-impact changes and require management sign-off for production changes. Integrate approval states into your ticketing system and enforce them before CI/CD pipelines or deployment tools will proceed.
- Logging, monitoring, and periodic review: Log all change activity (who, what, when), collect physical access logs (badge swipes, door sensors), and review them regularly. Conduct quarterly reviews of the authorized-personnel list and access rights. Revoke access immediately on role change or termination.
Example in a Small or Medium Business
Acme IT Services, a 60-person software company, defines a small change team responsible for production deployments: two senior sysadmins and the release engineer (Alice). The company documents in an "Access Authorizations" file that Alice may deploy updates to production web servers and that senior sysadmins can perform network configuration changes; this file lists badge access to the server room and the specific servers each person may log into. Acme's change policy requires testing in staging, a change ticket with a description of the change, and approval from the engineering manager plus one member of the CAB before production execution. The deployment window is restricted to the last Friday of each month between 5:00 PM and 8:00 PM; the deployment tooling will not run outside that window. Physically, server room doors require badge access and a sign-in sheet for any visits during change windows; logically, administrators use a jump host with MFA and PAM to access production servers, and temporary credentials are issued and recorded in the ticket. After each deployment, logs from the deployment system, PAM sessions, and door access are collected and reviewed to confirm only authorized people performed the approved change. Quarterly, HR and IT review the authorization file and remove privileges for people who moved roles.
Summary
Defining, documenting, approving, and enforcing both physical and logical access restrictions for system changes reduces risk by ensuring only the right people can make approved changes at approved times. For SMBs this translates to a practical mix of simple policy documents (access authorizations and change windows), lightweight approval workflows, and enforceable technical controls—MFA, RBAC, PAM, jump hosts, and logging—backed by periodic reviews. Together these policy and technical measures create an auditable, manageable process that meets the control while remaining realistic for small IT teams.