NIST SP 800-171 & CMMC 2.0 3.13.10 Requirement:
Establish and manage cryptographic keys for cryptography employed in organizational systems.
NIST SP 800-171 & CMMC 2.0 3.13.10 Requirement Explanation:
Cryptographic key management system provide for the management of cryptographic keys including generation, distribution, storage, backup, archive, recovery, use, revocation, and destruction. Examples of cryptographic keys include SSH keys, PGP keys, and digital certificates. The first intent of this practice is to ensure cryptographic keys are properly created in a secure manner that prevents them from being reproduced by an adversary. The second intent of this practice is to ensure cryptographic keys are managed in a secure manner that prevents them from being stolen by an adversary. Key establishment involves the creation of keys and coordination among parties that will use the keys of the methodology for generating the final keying material. Key management involves protecting keys when they are distributed when they are stored when they are being used, and when they are being recovered.
Example NIST SP 800-171 & CMMC 2.0 3.13.10 Implementation:
Examples of cryptographic keys include SSH keys, PGP keys, BitLocker keys, and digital certificates. Create an inventory of your cryptographic keys and determine who is responsible for which keys. Create a policy covering the life cycle of your encryption keys. If you do not have many keys, you can accomplish this manually.
NIST SP 800-171 & CMMC 2.0 3.13.10 Scenario(s):
- Scenario 1:
Your company uses SSH keys to access its server and network devices. To prevent an attacker from accessing the keys you use a key management system and have a robust key management policy. In accordance with your policy, new keys are generated every few months. Only authorized individuals are provided the keys. They are not allowed to provide it to others. Your policy states that keys must stored in an encrypted format. Your key management system handles the distribution storage, backup, use, revocation, and destruction of keys. This is more efficient than a manual process.
- Scenario 2:
You encrypt all of your company’s Windows computers Bitlocker. As you configure encryption on each device, it generates a cryptographic key. You associate each key with the correct computer in your inventory spreadsheet and restrict access to the spreadsheet to the system administrators whose work role requires them to manage the computers.
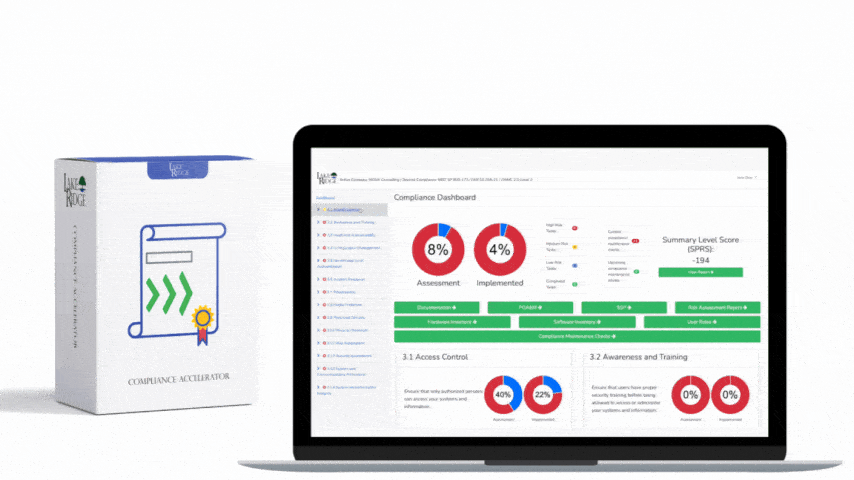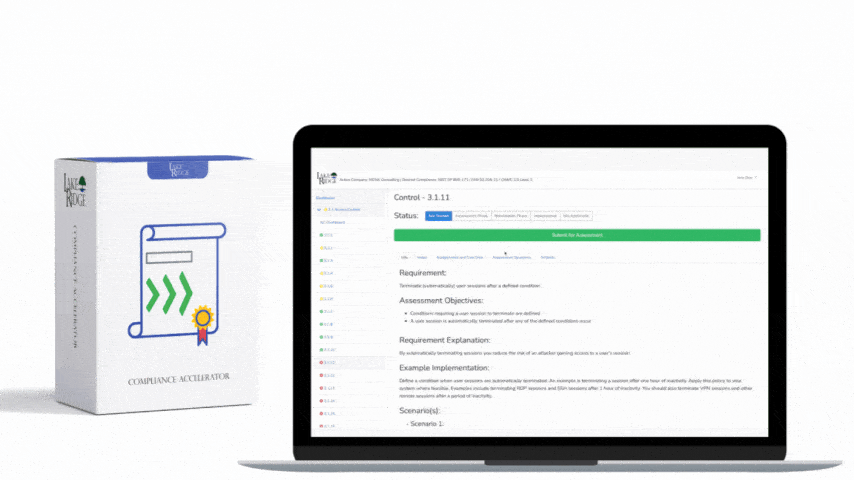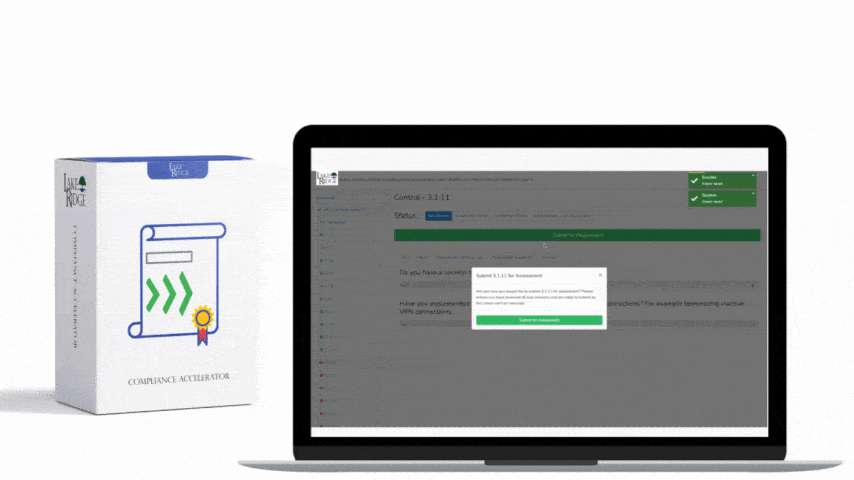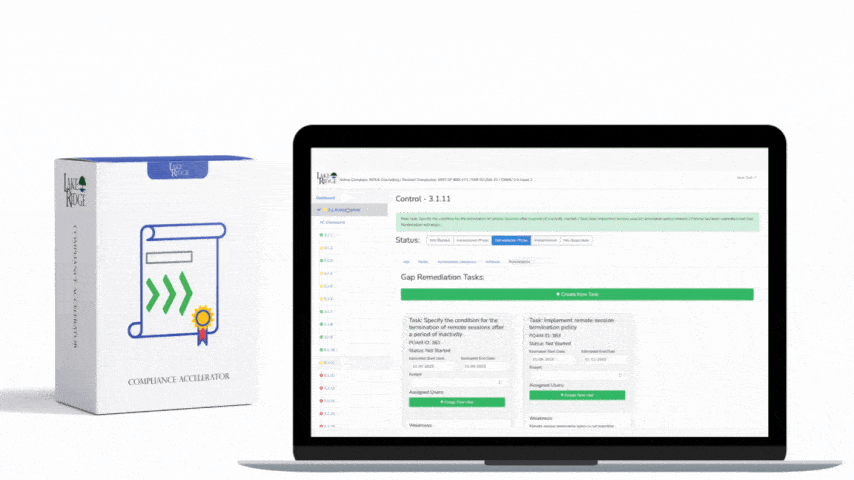
Quick & Simple
Discover Our Cybersecurity Compliance Solutions:
Whether you need to meet and maintain your compliance requirements, help your clients meet them, or verify supplier compliance we have the expertise and solution for you