To meet your NIST SP 800-171 requirement 3.8.3, you must “sanitize or destroy information system media containing CUI before disposal or release for reuse.” The objective of this requirement is to ensure that your data can not be recovered from media such as paper documents, removable drives, and hard drives when they are disposed of or reused.
What is System Media?
System media refers to physical devices or writing surfaces onto which information is recorded, stored, or printed within an information system. This refers to paper documents (non-digital media) and other devices that store information digitally (digital media). Examples of digital media include internal hard drives, external hard drives, USB thumb drives, and backup tapes.
What is Media Sanitization?
According to NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 1 “Guidelines for Media Sanitization” the term sanitization refers to a “process to render access to Data on media infeasible for a given level of effort.”
There are three types of actions that can be taken to sanitize media; these include clearing, purging, and destroying media.
Types of Media Sanitation
Clearing: applies logical techniques to sanitize data in all user-addressable storage locations for protection against simple non-invasive data recovery techniques; typically applied through the standard Read and Write commands to the storage device, such as by rewriting with a new value or using a menu option to reset the device to the factory state (where rewriting is not supported).
Clearing is used on digital media. An example of clearing is the use of the DoD 5220.22-M wipe method on a drive. This method writes random data on the drive.
Purging: applies physical or logical techniques that render Target Data recovery infeasible using state of the art laboratory techniques.
Purging is also used on digital media. An example of purging is to use a degausser on a hard disk drive or using a cryptographic erase function on a device.
Destruction: renders data recovery infeasible and results in the subsequent inability to use the media for storage of data.
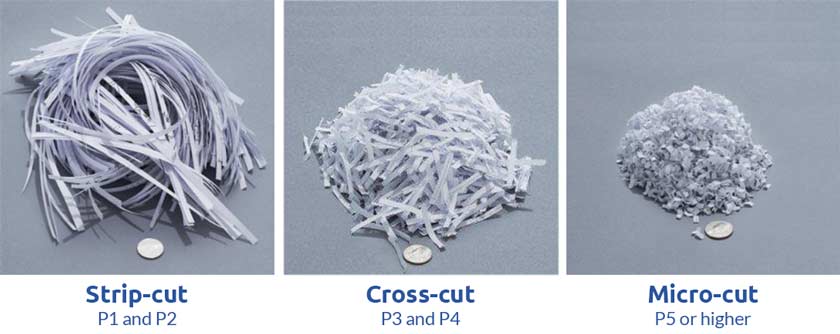
Destruction is used on digital and non-digital media. Digital media that is physically destroyed is either disintegrated, pulverized, melted, or incinerated. Non-digital media such as paper containing CUI is shredded using cross-cut shredders which produce particles that are 1 mm x 5 mm (0.04 in. x 0.2 in.) in size (or smaller), or pulverized/disintegrated using disintegrator devices equipped with a 3/32 in. (2.4 mm) security screen.
Selecting a Sanitization or Destruction Method
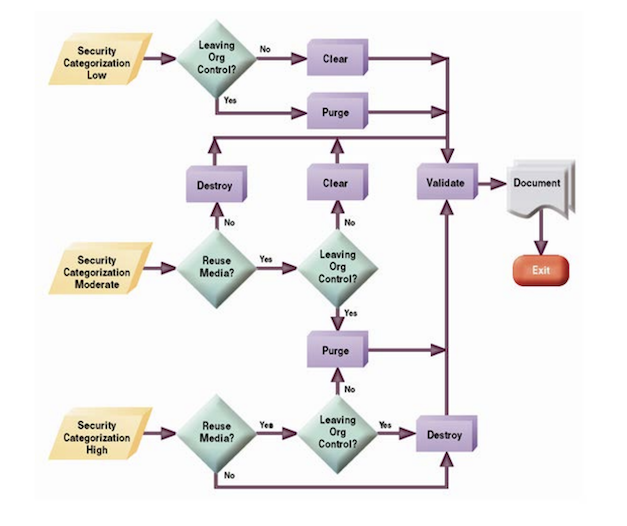
If you are going to reuse a device within your organization you do not need to completely destroy the device. The method used for destroying your media is dependent on where the media will go and the security categorization of the data stored on the media. The below diagram is quite useful.
Documenting Sanitation and Destruction
You should document the destruction of media in a “certification of sanitation” (download our template). If you paid a third party to destroy your media (e.g., hard disk shredding) then you should receive documentation from them verifying that your media has in fact been destroyed.
Referenced Resources